AndrewNG Course-Supervised Machine Learning: Regression and Classification, Quick Keypoints:
#WEEK-1
1-What is machine learning?
"Field of study that gives computers the ability to learn without being explicitly programmed"
The two main types of machine learning are supervised learning and unsupervised learning.
Teaching about learning algorithms is like giving someone a set of tools and equally important, so even more critical to making sure you have great tools is making sure you know how to apply them because like it is somewhere where it gives you a state-of-the-art hammer or a state-of-the-art hand drill and say good luck.
2- Supervised Learning
Supervised machine learning, or supervised learning, refers to algorithms that learn x to y or input to output mappings.
The key characteristic of supervised learning is that you give your learning algorithm examples to learn from. That includes the correct answers, whereby the right answer, I mean, the correct label y for a given input x, and is by seeing the correct pairs of input x and desired output label y that the learning algorithm eventually learns to take just the input alone without the output label and gives a reasonably accurate prediction or guess of the output
There's a second major type of supervised learning algorithm called a classification algorithm.
3- Unsupervised Learning
Were given data that isn't associated with any output labels y, say you're given data on patients and their tumor size and the patient age. But not whether the tumor was benign or malignant.
Why in the dataset, instead, our job is to find some structure or some pattern or just find something interesting in the data. This is unsupervised learning, we call it unsupervised because we're not trying to supervise the algorithm.
An unsupervised learning algorithm might decide that the data can be assigned to two different groups or two different clusters. And so it might decide, that there's one cluster what group over here, and there's another cluster or group over here. This is a particular type of unsupervised learning, called a clustering algorithm. Because it places the unlabeled data, into different clusters and this turns out to be used in many applications.
For example, clustering is used in google news, what google news does is every day it goes.
And automatically figure out whether the major types of individuals, since we're not giving the algorithm the right answer for the examples in advance.
4-Linear Regression Model
| **General
| Notation** | Description | Python (if applicable) |
| 𝑎 | scalar, non bold | |
| 𝐚 | vector, bold | |
| Regression | ||
| 𝐱 | Training Example feature values (in this lab - Size (1000 sqft)) | x_train |
| 𝐲 | Training Example targets (in this lab Price (1000s of dollars)) | y_train |
| 𝑥(𝑖), 𝑦(𝑖) | 𝑖𝑡ℎ��ℎTraining Example | x_i, y_i |
| m | Number of training examples | m |
| 𝑤 | parameter: weight | w |
| 𝑏 | parameter: bias | b |
| 𝑓𝑤,𝑏(𝑥(𝑖)) | The result of the model evaluation at 𝑥(𝑖) parameterized by 𝑤,𝑏 𝑓𝑤,𝑏(𝑥(𝑖))=𝑤𝑥(𝑖)+𝑏 | f_wb |
5-Cost Function
In order to implement linear regression the first key step is first to define something called a cost function.
The cost function will tell us how well the model is doing so that we can try to get it to do better.
Visualising Cost Function
6-Gradient Descent
Implementing Gradient Desecnt-
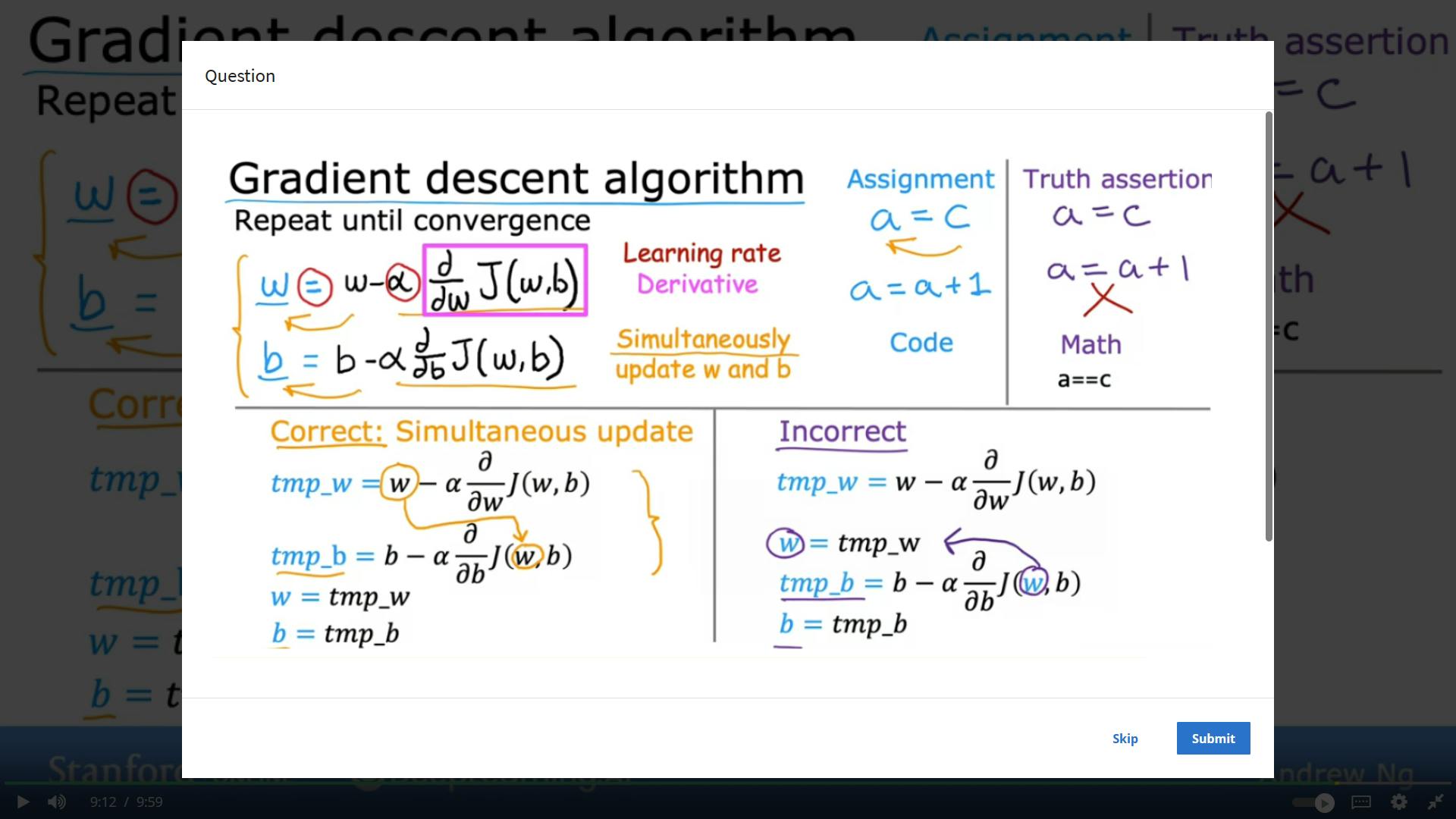
Gradient Descent Intutuion-